Search
Research
Systems pharmacogenomics identifies novel targets and clinically actionable therapeutics for medulloblastomaMedulloblastoma is the most common malignant paediatric brain tumour and a leading cause of cancer-related mortality and morbidity. Existing treatment protocols are aggressive in nature resulting in significant neurological, intellectual and physical disabilities for the children undergoing treatment. Thus, there is an urgent need for improved, targeted therapies that minimize these harmful side effects.

News & Events
Raine Foundation grants powering child health researchValuable support from the Raine Medical Research Foundation’s 2025 grant round will power four new research projects at The Kids Research Institute Australia.

News & Events
Big run ends, race for cure continuesOur local legend, brain cancer researcher Jacob Byrne, has crossed the finish line of his final marathon, completing his Big Run for Little Brains - 30 marathons in 30 days, covering 1266km across Perth’s local government areas.
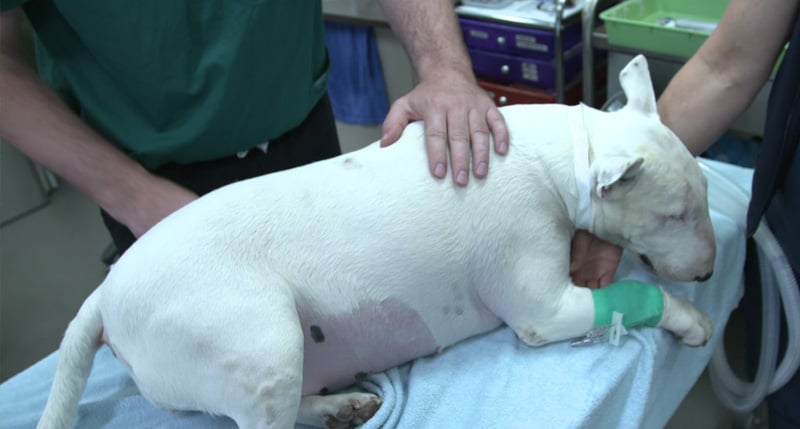
News & Events
World-first clinical trial in ‘man’s best friend’ could unlock treatment breakthrough for kids with cancerThe Kids Research Institute Australia is leading a unique clinical trial in pet dogs that could pave the way for a new immunotherapy treatment for one of the most common childhood cancers, Sarcoma.

News & Events
Trial of new antibody gives hope to children suffering from brain cancerChildren with aggressive brain cancers could soon have access to a significant new treatment option, using a unique antibody that stops cancer cells from repairing themselves.

News & Events
Cancer Council WA supports development of less toxic treatments for childhood brain cancerThe Kids Research Institute Australia researcher, Dr Raelene Endersby, will work to develop less toxic treatments for children with brain cancer, thanks to support from Cancer Council WA.

News & Events
The Kids Research Institute Australia Cancer Centre Researcher wins Cancer Council WA FellowshipCancer Council WA has awarded a Post-Doctoral Fellowship to Dr Ben Wylie, for his project to help kids with sarcoma.

News & Events
“Natural killer” donor cells fighting kids leukaemiaNew research by The Kids shows donor immune cells are highly effective at boosting the body’s response against leukaemia.
Research
Determining risk features for medulloblastoma in the molecular eraNick Gottardo MBChB FRACP PhD Head of Paediatric and Adolescent Oncology and Haematology, Perth Children’s Hospital; Co-head, Brain Tumour Research
Research
Viridans Group Streptococci in Pediatric Leukemia and Stem Cell Transplant: Review of a Risk-stratified Guideline for Empiric Vancomycin in Febrile NeutropeniaViridans group streptococci (VGS) are an important cause of sepsis in immunosuppressed children. We reviewed the effectiveness of risk-stratified addition of vancomycin to empiric febrile neutropenia therapy among 107 children with leukemia or undergoing an allogeneic transplant.
